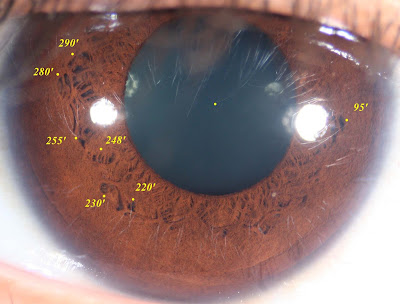
Multiple lacunae & crypts attached around the external border of the collarette is a typical sign of Polyglandular structure. You may explain the general disease tendencies for this structure and concentrate on explore those smallest signs, co-signs and indented signs which attached on the external border of the collarette. In addition, explain the physical & emotional levels of erratic of hypertrophy collarette structure. Please compare your previous post findings : (ssl) -1, 2 & 3 compile together to achieve more comprehensive iris assessment.
1) In this case, Polyglandular Weakness Type, the possibility genetic weaknesses tendencies as follow:
a) Diabetes Mellitus
b)Hypothalamus stress
c) Pituitary weakness
d) Endocrine system imbalance
e) PCOS (checking for family medical history)
f) Breast (checking for family medical history)
g) Kidney & Adrenal
i) Liver & Spleen
2) Observe the smallest iris signs ( crypt, lacuna, defect sign), co-sign with melanin pigment & indentation.
a) Double lacunae co-sign with melanin pigment at 95' indicate family history of high cardiovascular risk plus probability involvement with parental emotional conflicts.
b) Lacuna co-sign with melanin pigments attached on the external border of the collarette at 132' indicate with dual organs weakness - pancreas and spleen (pigment attached to spleen topography area).
c) Sharp indentation of the lacuna at 190' contrast with local indentation of the collarette at 180' signify insufficiency of kidney.
f) Melanin pigments relate to liver & gall bladder deficiency.
g) Lacunae & crypts encompassed with smaller melanin pigments at 235' & 250' represent pancreatic dysfunction.
h) Moderate indentation of the collarette co-sign with lacuna accompanied with brown pigment at 257' as a vital multidimensional iris sign
- Physical indicate thyroid dysfunction
- Negative emotion relate to sadness and pain
- Suppression of the emotional experience in connection to the trauma
- Time Risk at the aged of 19, possible with deep familial conflict
i) Observe lacuna at 280' that relate to heart problem
3) Explain the erratic & hypertrophy of the collarette structure..